Introduction
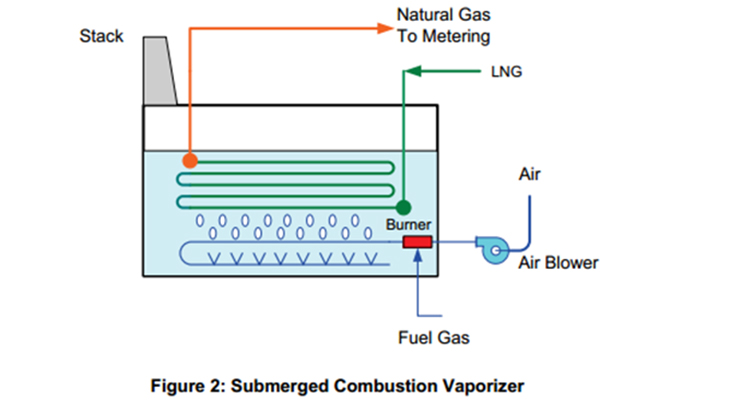
A typical SCV system is shown in Figure 2. LNG flows through a stainless steel tube coil that is submerged in a water bath which is heated by direct contact with hot flue gases from a submerged gas burner. Flue gases are sparged into the water using a distributor located under the heat transfer tubes. The sparging action promotes turbulence resulting in a high heat transfer rate and a high thermal efficiency (over 98%). The turbulence also reduces deposits or scales that can build up on the heat transfer surface.
Advantages
SCV units are proven equipment and are very reliable and have very good safety records. Leakage of gas can be quickly detected by hydrocarbon detectors which will result in a plant shutdown. There is no danger of explosion, due to the fact that the temperature of the water bath always stays below the ignition point of natural gas.
Main process parameters for SCV
| LNG capacity | 200T/h |
| LNG density | 0.44X1000Kg/m³ |
| LNG outlet temperature | 100℃ |
| Sea water pump power | 1500KW |
| Sea water pump capacity | 8930m³/h |
| Inlet& outlet pressure | 0.7MP |
Process Flow